Exploitation of ecological potential of natural systems isn’t traditionally included into the system of nature management, however, clean air, water, products of nutrition are the same natural recourse, it is widely spread at certain territories, and it is rare at different ones, and is also exhaustible, just as any other recourse. Is bearer is the nature’s ability to self-recover. The greater is an ecosystem’s stability potential, the more clean air, water, and nutrition is available to human.
In order to limit unreasonable destruction of nature’s potential, it is necessary to maximize convergence between indexes of financial-economic efficiency and ecological safety of any types of activity. Initial possibility of such combination is linked to a high correlation between indexes of economic efficiency of lands and their stability that exist in such conditions of natural ecosystems, it allows one to use land and rent taxes foe ecologic purpose. The system of differentiating land tax rates by the state, Federation subjects, and city municipalities that considers not only agrarian-industrial and infrastructural, but also ecological criterions, will provide for shrink of areas, occupied by producers, mainly due to refusal to use low-efficient or unequipped territories. At the same time a land and its ecosystems obtain a real significance for all categories of managers. Anthropogenic impact of human is unfavourable for the environment. The goal of this research is to give an evaluation of ecological potential of Russia and human impact upon the environment. This topic is urgent, as the problem of healthy existence of a person is faced at the modern stage of social development. Basic sources of polluting urbanized territories are industrial wastes that form as a result of productive process. Wastes of industry have a negative impact upon almost all components of the environment.
Development of recycling allows us to increase volumes of secondary raw materials, used on a territory, decrease costs of burning and burying wastes of production and consumption, increase power intensity of economy, increase investment attraction, decrease threat towards population health, create new jobs, decrease pollution of regional ecosystems, improve aesthetic condition of territories – all these possibilities allow us to consider recycling as one of important tools of solving ecological-economic problems, urgency of which increase with greater rates than efficiency of the implemented measures does.
During any industrial production solid industrial wastes (SIW) are formed inevitably. Some enterprises use SIW partially in adjacent or basic productions, and they might not be used at all. Thus, accumulation of SIW of different types and conditions takes place inevitably at enterprises, and they need to be utilized – burnt, buried, or taken to a fill. Over 340 million of industrial waste of different types and classes of hazard are produced at the territory of Krasnodar region annually. Basically, the established volumes are buries, and, of course, it has an effect upon the ecological situation in the region. Most utilization grounds do not correspond to modern international norms and rules.
According to statistic data of observing industrial wastes and their consumption, provided by the Administration of federal service of observing in the area of natural usage in Krasnodar region, types of solid industrial wastes that are discharged at the region territory in 2011, have been defined. Danger class of industrial wastes that is defined according to requirements of hygienic and radioactive safety, has been considered while revealing wastes [1].
In order to estimate recycling ability of the selected SIW, indexes that define an ability of secondary use, have been defined for each type of wastes. Such in dexesare: coefficient of for mingrelations Kb and criterion parameter of quality Kc that depends on means and conditions of preparing waste for further processing. In order to analyze relations between these indexes and reveal the most recycle-efficient wastes, we have implemented the method of ranging correlation [2].
The results of ranking SIW of Angaro-Enisey region according to coefficients of forming relations Kb and criterion parameters of quality Kc are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Results of ranking SIW
|
Number |
Waste type |
Kb |
Kc |
Ranks of variable indexes |
Differences between ranks |
||
|
i |
yi |
xi |
wi |
vi |
(vi – wi) |
(vi – wi)2 |
|
|
1 |
Wood chips |
0,99 |
85 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
9 |
|
2 |
Sawdust |
0,96 |
87 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
|
3 |
Crust |
0,9 |
90 |
3 |
1,5 |
–1,5 |
2,25 |
|
4 |
Vermiculite |
0,82 |
90 |
4 |
1,5 |
–2,5 |
6,25 |
|
5 |
Glass |
0,8 |
80 |
5,5 |
6 |
0,5 |
0,25 |
|
6 |
Plastics |
0,8 |
72 |
5,5 |
7 |
1,5 |
2,25 |
|
7 |
Polyethylene terephthalate |
0,75 |
81 |
7 |
5 |
–2 |
4 |
|
8 |
Rubber-technical products |
0,7 |
65 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
1 |
|
9 |
Wooden slag |
0,67 |
58 |
9 |
10 |
1 |
1 |
|
10 |
Coal slag |
0,6 |
67 |
10 |
8 |
–2 |
4 |
|
11 |
Garbage burning slag |
0,33 |
23 |
11 |
11 |
0 |
0 |
|
12 |
Haydite waste |
0,31 |
18 |
12 |
15 |
3 |
9 |
|
13 |
Gypsum waste |
0,3 |
20 |
13 |
13 |
0 |
0 |
|
14 |
Chamotte brick breaking |
0,22 |
20 |
14 |
13 |
–1 |
1 |
|
15 |
Wastes of solid polystyrene |
0,2 |
20 |
16 |
13 |
–3 |
9 |
|
16 |
Coke dust |
0,2 |
15 |
16 |
16,5 |
0,5 |
0,25 |
|
17 |
Crushed stone of non-consumable shape |
0,2 |
5 |
16 |
19,5 |
3,5 |
12,25 |
|
18 |
Textile |
0,17 |
5 |
18 |
19,5 |
1,5 |
2,25 |
|
19 |
Wastes of processing ore and raw materials |
0,16 |
15 |
19 |
16,5 |
–2,5 |
6,25 |
|
20 |
Mineral sludge |
0,15 |
10 |
20 |
18 |
–2 |
4 |
|
Sum |
– |
– |
210 |
210 |
0 |
75 |
|
According to the data, presented by Table 1, we shall calculate ranking correlation coefficient of Spearman:
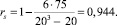
The received coefficient of ranking correlation nears + 1, and it testifies on a close relation between the coefficient of forming relations and criterion parameter of quality. Therefore, using these indexes to evaluate recycling possibility is reasonable.
In order to recycle SIW at the territory of Krasnodar region and in Angaro-Enisey district specifically, it is necessary to define, what types of waste can be used as secondary raw materials according to criterions of efficiency and ecologic safety. To solve this problem, we have implemented the method of ranking correlation with usage of Spearman coefficient and revealed types of SIW that can be used with no damage for human health by an output product [3].
Let us imagine a certain type of product, received with usage of SIW as a function of healthy characteristics of product components Bpr on types of waste, used while producing the given product. This functional dependence in normalized values of the factor looks as:
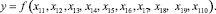
In natural values of the factor it looks as:
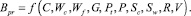
Table 2 presents the studied factors, waste types, and their sum volumes according to enterprises.
According to the provided correlation analysis with usage of ranking correlation coefficient of Spearman and the selection of solid industrial wastes, estimation of their recycling efficiency, we suggest measures that explain what types of SIW can be used in certain industries in order to receive certain products. It is possible to receive slabby materials with increased characteristics of solidity in case of breaking polyethylene terephthalate to definite granulometric composition and adding it into the contents of slabby production in range of 10 to 40 %. Thus, producing fibreboard of 2,5 mmthickness with addition of 10–20 % of polyethylene terephthalate will increease the board solidity to 75–90 MPa. Thus, it is possible to set up an output of slabby and block materials with increased indexes of solidity in case of implementing polyethylene terephthalate wastes without great investments.
It has been established that bass and crust, processed together via method of dry breaking to a certain granulometric composition and warming the received mass up to a definite temperature, one can receive a glue substance. Using the received composition in production of firbreboard makes it possible to produce plates of solidity characteristics, set by GOST, and also decrease wood material consumption, plates’ costs and toxicity while preserving physical-mechanic characteristics of the product. At the same time, plates’ appearance remains the same, and the problem of utilizing significant reserves of crust is solved.
Table 2
Initial matrix for statistic-mathematical analysis of SIW
|
Number |
Waste type |
Waste volume |
||||
|
Natural values |
Normalized values |
Natural values |
Normalized values |
|||
|
1 |
C |
Crust |
x11 |
89929,24 |
V1 |
x21 |
|
2 |
Wc |
Wood chips |
x12 |
1286889,07 |
V2 |
x22 |
|
3 |
Wf |
Sawdust |
x13 |
589138,58 |
V3 |
x23 |
|
4 |
G |
Glass |
x14 |
423,64 |
V4 |
x24 |
|
5 |
Pt |
Polyethylene terephthalate |
x15 |
1452,13 |
V5 |
x25 |
|
6 |
P |
Plastics |
x16 |
622,77 |
V6 |
x26 |
|
7 |
Sc |
Coal slag |
x17 |
650117,83 |
V7 |
x27 |
|
8 |
Sw |
Wooden slag |
x18 |
3217,17 |
V8 |
x28 |
|
9 |
R |
Rubber-technical products |
x19 |
615,76 |
V9 |
x29 |
|
10 |
V |
Vermiculite |
x110 |
290018,88 |
V10 |
x210 |
Thus, without breaking technological process, it is possible to set up an output of plate products, construction and finishing materials of special purpose that possess some additional characteristics at enterprises. It will allow one to increase productive powers of enterprises, decrease consumption of raw materials, cut costs while preserving physical-mathematic characteristics of products, broaden realization markets also due to western-European customers, increase product quality, decrease material and energetic costs of production. These measures can help improve the region’s ecology significantly due to utilizing wastes.

