The research manager for the institutionalization of corporate social responsibility (CSR) in countries with «transition» economies. Grounded components and stages of competence CSR manager. The basic professional competence CSR manager.
Transformation of relationships between government, business, and social sector go on in «transitive» economies of CIS countries. While large, especially city-forming enterprises carried out not only productive, but also social function, maintained social infrastructure, polyclinics, kindergartens, clubs, libraries, sport schools, etc. in times of planning economy, the society still expect enterprises (regardless of property form) will take responsibility for everything that goes on in their location in terms of transiting towards market economy [5]. Besides, more and more companies aim to support their socially-responsible image nowadays. As Western experience shows, a company’s reputation depends not only on its profit, but also on its activity in social and ecological area today. Therefore, the strategy of corporate social responsibility (CSR) has become key element of modern corporate management and obtains wider spread in CIS business areal.
The history of active CSR practice development in CIS, in our opinion, began in 2004–2005 due to expansion of corporate technical-scientific complex management and also actions of European Commission and specialized international organizations (Global agreement of UN, CSR Europe, etc). The period of accumulating corporate CSR experience, defining directions and scales of social investments, mastering world practices, and developing specific approached has been going on up to modern days.
On the one hand, in market conditions enterprises pay their taxes that should be transformed into social services by the government, and, on the other hand, they adopt social responsibilities within strategies of CSR, volume of which is defined by owners. However, carrying out significant social obligations draws resources, it decreases a company’s competitiveness of domestic companies at the world market [5]. Thus arises demand for specialists who are able to manage new directions of activity for CIS companies that implement CSR and work will all interested groups in coordinating their expectations and basic problems of business.
Head of the Center of corporate social responsibility of Business-University MIRBIS (Russia), Svetlana Gerasimova provides data of consulting company TRIOLIT Executive Search on the developing practical interest towards CSR managers and selecting social managers [2].
In 2006–2007 interest towards CSR area increases. While CSR managers have not been wanted earlier, nowadays HR agencies display positions for specialist as: PR director of foreign branch office of a holding; manager of coordinating corporate relations; deputy head of corporate relations department; head of department of relations with legal agencies; head of managing personnel and regional programmes; manager of ecological safety programmes.
The demand for CSR managers has decreased and shutting down non-profile programmes has been registered due to the crisis in 2008–2009. However, significance of CSR projects’ efficiency increases among companies, therefore, candidates of highest qualification are required: head of corporate charity fund; CSR program manager; head of division of personnel management; project supervisor of social policy department; head of external relations department (GR); head of managing operations with regional legal bodies.
In 2010 number of applications from HR agencies’ clients for CSR managers remained insignificant. Mainly, head managers of projects «Personnel reserve» and international PR-projects are wanted. However, a stable growth in demands for CSR managers has been observed in 2011–2012.
Nowadays this sector of labour market is not developed significantly in countries of CIS. Analysis of organization structures of Ukraine enterprises has shown that position of CSR managers exist only in several dozens of the largest companies, for example, «Pharmak», SKM, «Kiyevstar», «1 + 1 media», Ernst and Young, etc. [6–9].
At the same time, employers are not ready to accept specialist with no experience for this position. Thus, head of PR-service of company group «1 + 1» Svetlana Pevelitskaya says: «We have opened position of CSR manager in the end of August and closed it in the end of November, which is too long, since normally we close positions within two or three weeks [6]» About 200 resumes have been received during this period, and short-list included only 4–5 persons who had worked in large international enterprises, where CSR practices are ordered from HQ, and had a definite idea on principles of CSR work.
Growth in demand for professional managers of corporate social responsibility in Ukraine requires the quickest establishment of their training. Employers are even ready to invest into further CSR training of their employees and account such expenses in their budget [6].
Company group «System Capital Management» (SCM) initiated the process of introducing discipline «Corporate social responsibility» into educational programmes of institutions in 2009 [5]. Therefore, ministry of education and science of Ukraine (MESU) has ordered special operational group to develop a program for a new course «Corporate social responsibility» (CSR) for various circles of training as well as a complete set of methodical textbooks. MESU has recommended to introduce this academic course into educational plans of training specialists on courses «Economy and enterpreneurship» and «Management and administration».
The course program has been developed for future bachelors in economy and management as well as engineers (on initiative of National technical university of Ukraine «Kiev polythechnical institute») and presented on the 6th of November 2010 within the council, organized by the network of UN Global agreement in Ukraine and Ukraine Association of developing management and business-education (UADMBE). Coorganisators of the measure are economic faculty of Kiev national university of Taras Shvchenko, National university «Kiyev-Mogilyanskaya academy», Scientific-methodical commission of economy and administrating classical universities of Ministry of education and science of Ukraine [1].
Network «CSR in education» that has embraced 22 universities, has been created on intiative of the center «CSR development in Ukraine» and UADMBE with support of MESU, companies SKM and GA of UN gradually in 2009–2010 [8]. Over 60 institutions of Ukraine have started to teach CSR discipline during the latest four years.
Although disciplines of CSR have already been adopted by Ukraine institutions, operating specialist are forced to search ways to receive and confirm their knowledge. Therefore, Business Academy of CSR (CSR Academy) was founded in November 2012. It is a partner project of editorial office «Economika» (Ekonomika Communication hub) and center «CSR development in Ukraine», the first business school in field of corporate social responsibility and stable development in CIS [8–9]. Professional course on specialty of CSR manager (stable development manager) can be taken up on full- and part-time basis in 5 months in CSR Academy. According to organizers, such special course can be especially interesting for the whole business society: managers of PR, HR, GR, preservation of environment, protection of labour, employees of charity funds, coordinators of social and ecological programmes who can improve their qualification.
In 2012 University of economy and legal right «KROK» joined the global network (GD UN) on CSR, and National Classifier of Ukraine professions was enriched with three new specialties: «administrating manager on corporate social responsibility», «auditor of social work», «expert of social responsibility». And, since 2013 training masters on the program «Corporate social responsibility» was started for the first time in Ukraine in the university KROK: students, training on specialty «Administrative management» receive two qualifications – «Manager of administrative operations» and «Manager of corporate social responsibility» [6, 8].
Modern stage of institutionalizing social responsibility in Ukraine is described by the fact that MESU introduced normative (obligatory) social-human scientific discipline «Social responsibility» for masters in management, economy, and enterpreneurship in 2013. The course program includes topics on forming fundamental knowledge on theory and practice among students as well as professional competences on basic directions of social responsibility [4].
Of course, eight to ten years will pass before the market is filled with graduates, but such approach will allow us to receive trained professionals in field of CSR at Ukraine market, and not trust such a great responsibility to specialist of different specialties.
At the same time, as outlines Head of the Center of corporate social responsibility of PricewaterhouseCoopers of High School of Management of St. Petersburg state university Yuriy Blagov, «... structure of the basic CSR course for bachelors and masters of management, as well as MBA program attendants is pretty similar in Russia and the rest of the world. The main objective of the course is to present the idea of CSR as a system, in other words, give the definition of corporate responsibility, explain a manager’s part as one of a person who makes ethical and socially-significant decisions, point out organizational possibilities of managing corporate social activity at both state and global levels. In this case we can account on deep realization of CSR part in business and society» [7].
In our opinion, «manager of corporate social responsibility» (CSR manager) is a complex profession that requires not only a wide range of knowledge and competences, such as skills to form social dialogue and partnership, manage personnel and quality of products/services, understand a specific productive process, problems of non-financial report, etc., but also possess initially high moral qualities and an urge to «make the world better» as well as creative skills (Figure).
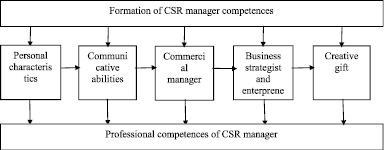
Algorithm of forming competences of corporate social responsibility manager
The presented algorithm of forming competence of CSR manager (Figure) is the basis of developing key professional competence – carrying out professional duties by CSR manager, a deep knowledge of theory and creative transformation of the accumulated practical experience of social responsibility.
According to experts in CSR, GR, HR, and PR [1, 6, 8, 10], as well as CSR practicians of Ukraine companies [2, 3, 5], analyzing training programmes of the course «Social responsibility» [4, 7, 9], has made it possible to define basic requirements towards CSR manager.
First of all, candidates for a position of CSR manager must respond not only to general requirements (Figure), such as: good basic education, analytic way of thinking, communicativeness, a skill to work in team, orientation towards economic, ecological, and social result, urge for professional growth and continuous self-development, etc., but also possess overall knowledge in the area of social responsibility.
The complex of such skills and knowledge includes competences, presented in Table in separate blocks.
Key professional competences (functional duties) of corporate social responsibility manager
|
Direction blocks |
Knowledge |
Skills |
|
CSR strategies |
Concept of stable development; global, regional, and national initiatives in CSR; international, European, and national law in CSR; worldwide and national CSR ratings |
Developing, renewing, and maintaining policy of a company in the area of stable development; developing CSR strategy; developing technologies of integrating CSR into business-strategy of a company; maintaining CSR budget; efficiency of CSR projects; CSR monitoring |
|
CSR programmes |
Models of managing CSR, introducing CSR practices into the area of personnel management, decrease in ecological impact, increase in efficiency of social costs, promoting principles of CSR and ethical business practices, business-practices of fighting corruption, principles of interacting with local societies |
Developing and realizing social programmes, corporate charity, ecology and industrial safety, involving employees through corporate volunteer service, private operational practices, responsible interactions with suppliers, socially-ethical marketing, programmes of personnel development / decrease in staff deficit, personnel health and safety |
|
Relations with stakeholders |
Developing map of stakeholders, international policies and practices of interacting with stakeholders |
Corporate policies and practices of interacting with stakeholders, collaboration and dialogue with stakeholders (forming constructive relations in terms of CSR); developing and realizing development projects at local and national level |
|
PR-CSR |
Preparing information and declaring social responsibility, presenting CSR as a specific advantage, increase in clearness of a company’s activity |
Introducing communicative program on CSR, internal consultation of employees, reputation management, coordinating social responsibility of departments and channels, interacting with national and international profile institutions, CSR communications through social networks |
|
Social reports |
International standards of CSR, standards and training non-financial reports |
Introducing social (non-financial) reports, training and promoting CSR reports, composing integrated reports |
Secondly, developing corporate strategy of social responsibility at the basis of stable development that implies that a company does not only put effort into its own development, but also considers interests of various involved parties. In our opinion, it is reasonable to refer to major international standards in CSR area in this case: Global agreement (GA) of UN (Global Compact), GRI (Global Reporting Initiative), SA 8000 (Social Accountability International’s), ISO 14000 (International Standarts Organization), AA 1000 (AccountAbility).
Using the most complete and newest international standard ISO 26000:2010 «Managing social responsibility» has a special significance [10]. ISO 26000:2010 aimes for preserving the seven principles of modern social responsibility: accountability, clarity, ethical behavior, maintaining international norms of behavior, securing human rights. Also, the standard indicates and explains basic topics of social responsibility that include 7 points as well: organizational management, reliable business practices, human rights, environment, labour practices, participation in life of societies and their development, problems, linked to consumers.
Thus, corporate social responsibility becomes a key factor of modern corporate management, but carrying out significant socially-responsible obligations draws resources, and it decreases competitiveness of our domestic companies at global market. Therefore, in order to adapt corporate management to international standards, position of corporate social responsibility manager is introduced into leading companies of CIS countries.
The work is submitted to the International Scientific Conference «Problems of international integration of national education standards», France (Paris), December, 21–28, 2013, came to the editorial office оn 13.12.2013.
Библиографическая ссылка
Yevtushenko V.A. MANAGER OF CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY: institutionalization and professional competence // Международный журнал экспериментального образования. 2014. № 4-2. С. 84-88;URL: https://expeducation.ru/ru/article/view?id=5103 (дата обращения: 21.02.2026).

