The requirements for the efficiency and durability of the concrete structures have already led to the widespread use in the cements with the mineral additives construction [3]. So, the mineral supplements are practically involved in the hydration reactions, as well as are made their influence on the concrete structures formation. The active mineral supplements are relative slowly involved in the hydration processes. Many authors have already noted the kinetics slowdown of the early strength cements with the mineral additives [2, 4]. The mineral additives are practically performed the fillers’ function in the concrete for a long time [4]. The mineral supplements poly-functionality is usually explained by the heterogeneity of their mineralogical, phase, and particle-size distribution. For example, that there is some portion of the inert impurities, in the form of quartz, feldspar, mullite in the natural and technogenic pozzolans [1].
The Purpose of the Study. The purpose of the study – is to be improved the cements use efficiency with the mineral additives. In practice, the mineral admixtures cements are the most commonly used, having obtained by the co-milling, and their specific surface area is determined, in general. For all this, it is not quite clear, what the specific surface area of the cement clinker part and the mineral supplement are, separately. To be identified the role of the specific surface area of the binder components, it can be possible at the cements splitting use grinding.
The main objective has been to be studied the specific surface area influence and the mineral additives content on the structural ceramsite concrete properties.
Materials and methods of research
For the experiment, it has been used the separately blended cement grinding, having contained, as the mineral inert supplement 50 % quartz filler. So, the clinker of the cement production of the CJSC «Ulyanovskcement» (Russia) with the specific surface area 400 m2/kg has had the following mineralogical composition: C3S = 59 %, С2S = 16 %, C3A = 8 %, C4AF = 13 %.
The studies have been performed on the ceramsite concrete dense structure, with the flow rate 0,9 m3 expanded clay in 1 m3 concrete. The samples of the 100×100×100 mm size cube have been molded from the aggregate ceramsite concrete mixtures. The ceramsite concrete compressive stress has been determined after the ceramsite humid heat treatment duration (e.g. 4 + 2 + 8 + 2) hours at the isothermal heating temperature 90 °С. The ceramsite concrete average density has been determined in the dry condition.
Results of research and their discussion
The specific surface area influence of the quartz filler and its content on the compressive strength of the structural ceramsite concrete has already been studied. During the three-factor plan experiment execution, the mixed cement content (Х1) has been varied within the limits from 200 up to 600 kg per 1 m3 concrete, the specific surface area of the quartz filler (Х2) has been changed from 100 up to 900 m2/kg, the aggregate concrete mixtures stiffness (Х3) has been ranged within the limits from 5 up to 25 seconds on the technical viscometer.
At the confidence probability level 95 %, the polynomial regression model has been obtained, depending on the caramsite concrete compressive strength (Y), MPa, from the variable parameters, which has the following form:
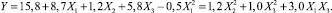
So, the graphic dependence of the ceramsite concrete compressive strength of the investigated parameters has been shown in the Fig. 1.
So, the obtained results’ analysis has been shown, that all the variable factors are quite significant. The cement content of the concrete and the concrete mixture stiffness are the most significant factors. The carried out studies have already been shown, that the specific surface area increase of the quartz filler in the range from 100 up to 500 m2/kg, is promoted the increase ceramsite concrete strength over the whole entire change range of the cement content. The further increase in the specific surface area of the filler in the range of 500 up to 900 m2/kg is hardly affected the ceramsite concrete strength. It, moreover, has been established, that the influence degree of the specific surface area of the filler on the ceramsite concrete strength is depended on the cement content: the smallest increment of the concrete strength (e.g. about 6 %) is observed in the compounds with the mixed cement content 600 kg per 1 m3 of the concrete (e.g. 300 kg of the clinker cement). When the content of the mixed cement is equal to 200 kg per 1 m3 of the concrete, the growth concrete strength from the specific surface area increasing of the filler has been made up 18–80 %. So, the less increase of the strength (e.g. 18 %) has been observed in the mixtures with its stiffness of 25 seconds.
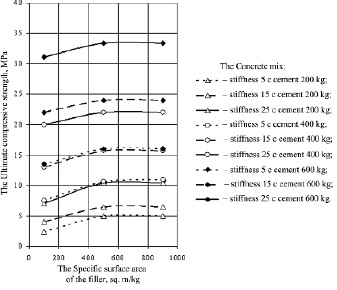
Fig. 1. The Specific Surface Area Influence of Quartz Filler on the Compressive Ultimate Strength of the ceramsite concrete, MPa, based on the Cement with Filler Content 50 %
The content influence and the specific surface area of the quartz filler in the ceramsite concrete compositions separately with low (e.g. 150 kg) and high (e.g. 450 kg) content of the clinker cement has been studied. The ceramsite concrete compositions, having prepared from the stiffness mixtures of 15 seconds have been compared. The quartz filler has been entered into the compositions with the specific surface area 100 and 500 m2/kg, in the amount of 50…259 kg per 1 m3 of the concrete. The quartz filler content influence, its specific surface area and the content of the super-plasticizer C-3, in the amount of 0,5 % from the cement weight on the compressive ultimate strength of the ceramsite concrete have been shown in Fig. 2.
The obtained results’ analysis has been shown, that at the cement content in the 150 kg concrete the increase in the amount of up to 150 kg filler is been led to the increase of the ceramsite concrete strength. So, the carried out studies have been shown, that the filler with the specific surface area 500 m2/kg have been allowed, to a greater extent, to be improved the concrete structure strength and its seal. The specific surface area and the filler content influence on the concrete’s average density have been shown in the Fig. 3.
At the high content of the cement clinker part (e.g. 450 kg/ m3), the introduction up to 150 kg of the quartz fillers is hardly changed the concrete density and its strength. For all this, it is quite advisable to be used the filler with its specific surface area 100 m2/kg, at the energy consumption reduction for the filler grinding. Thus, the obtained result has its great significant for the compounds optimization of the self – compacting concrete types.
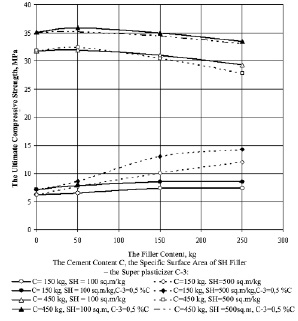
Fig. 2. The Quartz Filler Content Influence, its Specific Surface Area, and 0,5 % from the Super-plasticizer C-3 Cement Weight on the Compressive Ultimate Strength of the Ceramsite Concrete, MPa
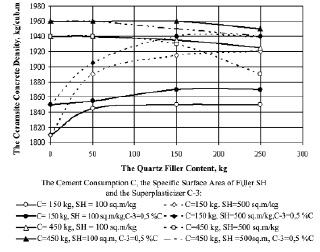
Fig. 3. The Quartz Filler Content Influence, its Specific Surface Area and Super – Plasticizer C-3 Presence on the Ceramsite Concrete Average Density
Conclusions
Thus, the already performed experiment has already been shown, that the fillers are practically led to the concrete strength growth, if they are increased its density. The specific surface area and the fillers content influence on the structural ceramsite concrete strength are completely depended on the cement consumption in the concrete.

